The swelling in the lower third of the face mandible crossed the midline and reached the opposite mandibular body region with buccolingual expansion. The child presented with a painless bluish and swelling in the sublingual and submental region with complaints of protrusion of tongue.

Computed tomography CT showed several round calcified foci.
Swelling in submental region. Swelling at the submental node is often a sign of disease and can be caused by numerous factors like an infected wisdom tooth oral cancer a tooth abscess oral infections lymphadenopathy leukemia lymphoma swollen lymph nodes and may also be a result of metastasis of cancer as reported by Right Diagnosis. The lump in the submandibular area is not too unusual. Nonmalignant swelling may be caused by mumps sialadenitis Sjögren syndrome cysts and infections.
Submandibular lymphadenopathy may also result from infections of teeth upper respiratory track sinuses and tonsils or infections mononucleosis. A sonogram of submental region revealed subcutaneous swelling in the submental region more on right side. Since patient was not willing for surgical treatment therefore advised to continue with the antibiotics and recalled after 5 days.
Patient revisited after 1 month with history of pus discharge 7- 8 days back. On inspection and palpation swelling had regressed. A 27-year-old male presented with a swelling in the submental region.
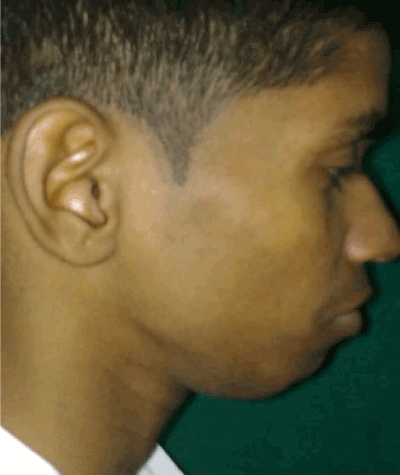
The submental swelling gave an appearance of a double chin. History revealed a trauma 5 years back which resulted in a painless mass due to hematoma under the chin. The masshematoma was initially less than 1 cm but gradually progressed during the following year.
Swollen submental lymph nodes are often very soft or tender warm and painful. When a submental lymph node swells rapidly it causes pain as a result of stretching. Sometimes the swelling brought about by their increase in numbers to fight infection may be less significant than the symptoms of the disease itself.
Submandibular swelling is a common clinical disorder of the maxillo-facial region that may be one of the manifestation of several pathologic disorders including sialolithiasis. A 38-year-old woman experienced a recurrent painful swelling in the. Itself as swelling in submandibular or submental triangle.
1- Marsupilization deroofing suture cyst wall to or al mucous m. 2- Excision difficult in recurrent cases. Inflammation Solid Multiple LNs especially swelling Neoplastic or metastatic 2 -Submandibular gland.
Midline cystic lesion if above the geniohyoid muscle is a sublingual swelling that will displace the tongue with consequent difficulty in eating and speaking. If the midline cystic swelling lies below the geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles will be a submental swelling and. Neck lumps Neck masses.
A neck swelling is any congenital or acquired swelling arising in the anterior or posterior triangles of the neck between the clavicles inferiorly and the mandible and base of skull superiorly. For the pediatrician the most frequently encountered sites of lymphadenopathy are the head and neck cervical lymphadenopathy. In the head and neck the submental and submandibular lymph nodes drain the tongue and floor of the mouth.
Their enlargement may be associated with a dental or periodontal source of infection. The cyst manifests itself as a sublingual swelling. When below the m uscle the clinical aspect will be a submental swelling 8.
Consequently tongue elevation speech altera tion or double-chin. The magnetic resonance images of each lesion revealed characteristic features. Thus MRI may be useful for the differential diagnosis of submental swelling before the initiation of treatment.
Various types of lesion have been reported in the submental region but submental masses can be difficult to diagnose. Signs and symptoms of a severe submental abscess include a firm swelling below the chin and dysphagia difficulty swallowing. Treatment is by surgical incision and drainage with the incision running transversely in a skin crease behind the chin.
We report a rare case of sublingual swelling in an 11 month old child which was a diagnostic and surgical challenge. The child presented with a painless bluish and swelling in the sublingual and submental region with complaints of protrusion of tongue. A pre-operative CT scan was done but a diagnosis was not truly established.
Causes of Submandibular Gland Swelling. If you feel swelling underneath your lower jaw it could be a swollen submandibular gland. Swollen submandibular glands are usually caused by tiny stones blocking the ducts that channel saliva into the mouth.
Dermoid Cyst of Submental Region Mimicking Pilomatricoma. Pilomatricoma is a skin appendage tumour which presents as midline swelling and is usually diagnosed with careful history and certain pathagnomonic features on fine needle aspiration cytology and ultrasonography. Hereby we are presenting a case of a submental swelling which was.
A painless soft swelling in the submental area usually indicates the presence of a thyroglossal duct cyst congenital sublingual dermoid cyst amyloidosis ranula or cystic hygroma. We described a case of relatively rare hemangioma with multiple phleboliths in the floor of the mouth presenting as a submental swelling. Abscesses of the second and third mandibular molars may perforate the mandible and spread into the submandibular and submental spaces.
Ludwigs angina is manifested by swelling of the floor of the mouth and elevation and posterior displacement of the tongueA rapidly spreading gangrenous cellulitis produces a brawny edema of the suprahyoid region of. A 28 year old male presented with a midline painless swelling in the submental region of the neck for 3-4 months. Examination of the neck revealed a non-tender soft mobile non-transilluminant swelling of 3 X 4 cm in the midline submental region.
The swelling was becoming prominent on contraction of the mylohyoid muscle and was not moving. Of the mouth presenting as a submental swelling. We report a case of 17-year-old Japanese female who presented with the mass in the submental region that had been slowly growing for several years.
The doppler ultrasonography revealed blood flow in the region. Computed tomography CT showed several round calcified foci. Objectives Various types of lesion have been reported in the submental region but submental masses can be difficult to diagnose.
Our objective was to attempt to diagnose submental masses by using magnetic resonance imaging MRI along with clinical data. Methods We attempted to diagnose seven cases in which the chief complaint was submental swelling. The swelling in the lower third of the face mandible crossed the midline and reached the opposite mandibular body region with buccolingual expansion.
Overlying skin color was normal with multiple healed fistulae with some micro-pigmentation in the right submandibular and submental region Fig. There was no active purulent discharge.